EV charging management software: What it is, how it works, and why it’s important for owners and operators
EV charging management software: What it is, how it works, and why it’s important for owners and operators
Upgrading your property with EV charging stations is a smart choice, but the key to seeing the full advantages they bring lies in their effective management. EV charging management software can help you streamline operations, save on energy costs, and keep your tenants and visitors happy.
Read on to learn more about this crucial element of EV charging infrastructure. This article covers the following topics:
- What is EV charging management software?
- Who benefits from using EV charging software?
- Important EV charging industry protocols and standards
- Use case spotlight: EV charging software for multifamily properties
- Examples of EV charging software in action
1. What is EV charging management software?
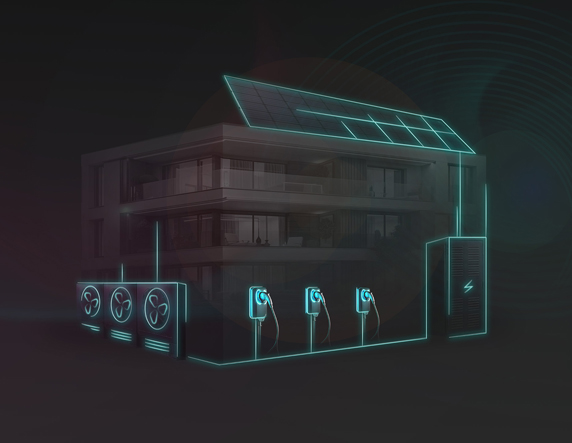
EV charging management software refers to specialized applications or platforms designed to monitor, control, and optimize electric vehicle (EV) charging stations. These software solutions are crucial for both EV drivers and site owners/operators, as they ensure a seamless, reliable, and efficient charging experience while optimizing operational management. Additionally, they can help reduce total ownership costs with smart energy management and process automation tools.
Depending on their particular features and service offerings, similar solutions might also be referred to (alt: advertised) as:
- EV charging station management systems (CSMS)
- Charge point management systems (CPMS)
- Charge point operator (CPO) platforms
- EV charging management solutions
Essentially, EV charging software solutions serve as the digital backbone of efficient, reliable, and sustainable EV charging infrastructure. They integrate with the physical chargers themselves and connect back to a centralized cloud-based management platform, streamlining everything from controlling access to adjusting fees to viewing real-time energy usage and much more.
Key components of an EV charging management platform
A comprehensive EV charging management software platform encompasses everything from user interfaces to back-office management, ensuring that charging stations operate efficiently and effectively. In essence, cloud-based charge point management systems can provide an end-to-end solution that includes:
- Charging station management software
- Billing & payment software
- Fleet management software
- User management & authentication software
- Smart charging & load management software
- EV driver software (such as mobile apps)
- Integration & API software
Having a single solution helps to unify all of the many factors that contribute to safe, effective, and reliable EV infrastructure. Those factors can vary depending on the use case, but often include things like distributing energy load, tracking charging activity, processing payments, etc.
Table: Types of EV charging management software
Minimizes grid impact, lowers electricity costs, and improves overall efficiency of charging infrastructure.
These software solutions collectively contribute to the efficient operation, management, and user experience of electric vehicle charging infrastructure across different scales and applications.
READ: Learn about some of the most important features to look for when selecting your software.
2. Who benefits from using EV charging software?
The short answer is: everyone. As the popularity of EVs continues to grow, most people in the U.S. and Canada will likely need to engage with some aspect of EV charging software. In the near term, however, certain groups stand to benefit the most from it. These include:
- Residential property managers: Apartment complexes and condo developments with shared parking facilities will need charging software to manage and allocate charging spots among residents, handle billing, and ensure fair access.
- Commercial property owners & real estate developers: Shopping malls, office buildings, and other commercial properties will benefit from offering EV charging as an amenity. Charging software helps manage these stations, handle payments, and provide a seamless user experience for customers or tenants.
- Utility companies: EV charging software helps utility companies by optimizing grid load through demand management, implementing tailored pricing models, improving customer engagement with user-friendly apps, analyzing data for grid planning, and supporting environmental goals and regulatory compliance.
- Transportation hubs: Airports, train stations, and bus terminals may offer charging stations for travelers and staff. EV charging software enhances user experience by offering convenient access to charging stations through mobile apps. It can also assist EV charger owners and operators by providing real-time monitoring of charging stations, optimizing availability for EV users, and potentially generating revenue through usage fees or partnerships with EV service providers.
- Government/public sector: EV charging software aids the government and public sector by facilitating the deployment and management of public charging infrastructure. It allows for efficient monitoring and utilization of charging stations, enables integration with smart grid technologies for grid stability, and helps in implementing policies that incentivize EV adoption through accessible and reliable charging infrastructure.
- Fleet operators: Companies that manage fleets of electric vehicles, such as delivery services of corporate fleets, will rely heavily on EV charging software to optimize charging schedules, monitor vehicle status, and ensure efficient energy use.
- EV owners: As the primary users, EV drivers will need access to a user-friendly interface that’s intuitive enough for them to understand and use without any specialized knowledge. Most charge point management software offers a mobile application for EV drivers to easily find and use charging stations and process payments on the go.
3. Important EV charging industry protocols and standards
As the electric vehicle industry grows, so too does the need for global regulations and standards for EV chargers and network interoperability.
Standardized charging protocols are essential for ensuring efficient and safe communication within the EV charging ecosystem. These protocols facilitate simplified access control and load management processes — making life easier for charge point operators (CPOs), EV regulators, e-mobility service providers (EMSPs), and EV drivers alike.
EV charging protocols are important because they help enable:
- Interoperability
- Efficient communication & data-exchange
- Seamless transactions
- Real-time monitoring
- Smart charging capabilities
- Safety
Achieving a steeper growth curve for electric vehicles hinges on ongoing technological advancements, increased commercialization, and effective regulatory policies. Standards and interoperability are fundamental to these trends, spanning vehicles, charging systems, and communication networks, thereby serving as pivotal drivers for electric vehicle adoption.
In the following section, we’ve compiled a list of crucial EV charging industry standards and protocols that provide the flexibility needed to support the entire electric vehicle market.
OCPP: Open-source, vendor-independent standard
Open Charge Point Protocol (OCPP) is an open communication standard between EV charging stations and a central management system.
Established by Open Charge Alliance (OCA) for the EV infrastructure market, it has emerged as a must-have standard for ensuring interoperability among EV charging manufacturers, charging network operators, and EV charging software providers.
Key versions:
- OCPP 1.6: Designed to establish basic interoperability and functionality.
- OCPP 2.0.1: Offers new and improved features for device management, transaction handling, security, smart charging functionalities, support for display and messaging, and the extensibility of OCPP. Also offers the option to support Plug-and-Charge (PnC) for electric vehicles supporting the ISO 15118 protocol.
Importance: Ensures interoperability between different manufacturers’ charging stations and central systems.
READ: Learn more about what exactly OCPP entails and why it matters.
ISO 15118: Bi-directional charging/discharging protocol
ISO 15118 is an international standard for digital communications between EVs and charging stations. More specifically, this protocol promotes a two-way power flow between electric vehicles and the grid.
First published in 2013 by the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), ISO 15118 defines communication protocols for Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology.
Key features:
- Plug-and charge (PnC) capability
- Bidirectional power transfer
- Secure communication
Importance: Enhances user convenience by allowing automated, secure authentication and billing, and supports advanced functionalities like vehicle-to-grid (V2G).
OpenADR: Energy management protocol
Open Automated Demand Response (OpenADR) is a standard for automating demand response and distributed energy resource management.
Key Versions:
- OpenADR 2.0: Enables standardization of demand response (DR) and distributed energy resource (DER) communications and automated processes.
Importance: Helps in balancing grid load by enabling utilities to manage the demand response of EV charging in real-time, improving grid reliability and efficiency.
OCPI: EV charging roaming protocol
The Open Charge Point Interface (OCPI) is a protocol for enabling communication between EV charging networks and service providers.
Key Versions:
- OCPI 2.2: Facilitates roaming, real-time exchange of charging station status, pricing, and reservation capabilities.
Importance: Supports scalability and reliability of electric vehicle charging networks by establishing common standards for communication and data exchange. Promotes seamless user experiences by allowing EV drivers to access and pay for charging services across different networks without the need for multiple accounts or subscriptions.
SOC II: Security compliance
SOC II is a framework for service providers to demonstrate secure data management and privacy protection practices.
Developed by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), SOC II (which stands for “System and Organization Controls” II) evaluates the internal systems and security controls a tech service business uses to protect customer data in the cloud.
Key features:
Audited controls include:
- Security measures
- Availability assurances
- Processing integrity validations
- Confidentiality protections
- Privacy compliance
Importance: Ensures service organizations securely manage customer data and meet criteria for trustworthiness.
4. Use case spotlight: EV charging software for multifamily properties
Large-scale adoption of EVs hinges on the simultaneous roll-out of accessible and affordable charging. According to a PwC analysis, the EV charging market in the U.S. will need to grow nearly tenfold — from somewhere around 4 million to an estimated 35 million chargers — to satisfy the charging needs of the 27 million EVs expected to be on the road by 2030.
Improving access to EV charging at home
Currently, the vast majority of electric vehicle charging occurs at home in the United States (83%) and Canada (80%) — where, due to the lower voltage 100-120V power grid in these regions, the ability to recharge in under ten hours requires installation of a dedicated charger.
Although implementing EV charging in single-family homes with onsite parking is usually relatively straightforward, it’s more challenging for the millions of multifamily properties that haven’t been properly futureproofed for EV charging.
In addition to space, parking structure, and logistical limitations, multifamily residential properties, also called multi-unit residential buildings (MURBs), can face complications around power supply, load control, connectivity and billing management — especially in older buildings.
Table: Barriers to EV charging at multifamily homes
Based on Government of Canada resource, Zero-Emission Vehicle Charging in MURB and Garage-Orphans
While no part of an end-to-end EV charging solution can make your building’s underground parking garage bigger or change the layout of your building’s electrical room, a quality EV charging software can handle billing, manage access, and balance the electrical load of multiple EV chargers.
5. Examples of EV charging software in action at multifamily properties
Looking for inspiration? Here are two case studies that show how different multifamily property owners, managers, and residents have leveraged EV charging software. From future-proofing their building and business for rising EV adoption to saving big by avoiding unnecessary electrical upgrades, these success stories demonstrate the true impact of today’s EV charging software.
The Lofts at Beacon: Future-proofing their building and business to easily manage rising demand
Management at The Lofts at Beacon, a residential redevelopment on the site of a former carpet mill, began hearing from residents about EV charging when work began on a second building on the property in 2022, adding 89 rental units to the 84 that were already onsite. “We started to get a lot of questions from people asking if we were going to install EV chargers,” said property manager Nicole Corneyea. “There were several people who were very excited about using them.”
To meet the demand for this increasingly essential amenity, The Lofts partnered with PowerUp EV Solutions to manage the project and oversee installation of 10 new electric vehicle chargers. In addition to being a great way to retain existing tenants and attract new ones, the chargers could also draw visitors looking to top up their batteries while they strolled through Beacon’s artist district or enjoyed nearby nature attractions. Once the necessary hardware was installed — and their chosen EV charging software system, from SWTCH, was fully operational — the chargers quickly became a popular addition to the property.
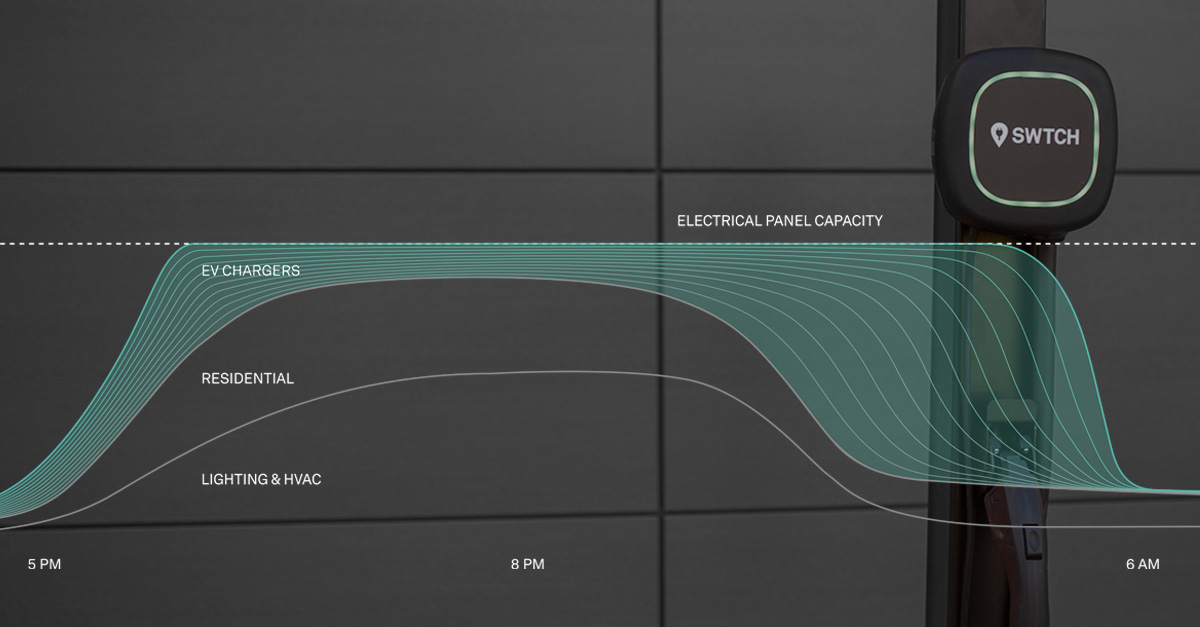
Thanks to SWTCH’s easy-to-use app, residents were able to start making use of the new chargers right away — and its scalable, hardware-agnostic software platform will simplify future expansion when there’s an inevitable increase in demand. For example, the 10 chargers onsite today are all on individual circuits. But with SWTCH ControlTM, The Lofts could expand to as many as 40 units through smart load management, with no need for electrical upgrades.
In the meantime, SWTCH’s software platform will provide management at The Lofts with essential visibility into metrics such as usage, demand, and kilowatts consumed by the chargers. This access to data will assist with ensuring service remains at the level of quality the building’s residents and visitors expect, and will also empower them to make more informed decisions about future expansions
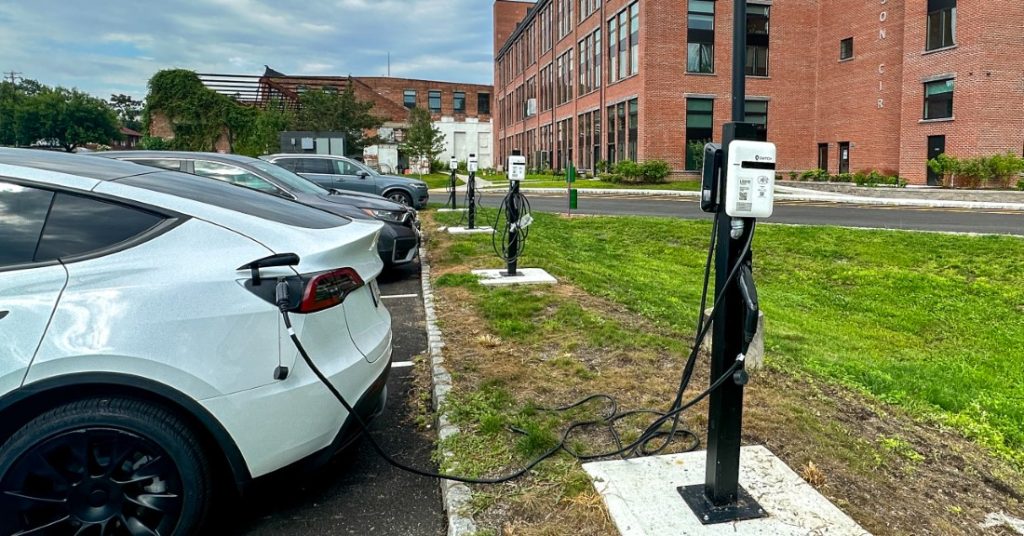

Read the full The Lofts at Beacon case study to learn how the 173-unit apartment complex integrated connected EV chargers to meet resident demand and future-proof their building and business.
New Times Square: Getting their MURB EV-ready while avoiding cost-prohibitive electrical upgrades
When New Times Square — a 375-unit condominium complex located in Toronto, Ontario — decided to retrofit their 20-plus-year-old MURB for EV charging, its property managers, condo board and residents were challenged by the logistical and infrastructure constraints this posed.
All parties knew they needed a plan to move forward. But with questions about electrical upgrade requirements, cost sharing responsibilities, and long-term management, the headaches seemed endless. It’s this exact point of tension between old and new that end-to-end EV charging software solutions were created to alleviate.
After extensive consultation to understand the limitations and needs of the building, the first step of the process was identified: get the building’s electrical infrastructure updated. New Times Square recognized the importance of investing in a long-term solution. That’s why, in addition to installing 21 private EV chargers for immediate use, they worked with their chosen EV charging service provider, SWTCH, to design infrastructure capable of supporting up to 40 chargers.
The key to being able to carry the charging load of 40 MURB EV chargers is due to SWTCH Control, our intelligent load management solution that dynamically adjusts the energy used for the chargers based on real-time usage. For instance, in the most extreme scenario, if 40 chargers are in use at once, the maximum output will be 8 Amps. If only 20 chargers are in use the output goes up to 16 Amps. Additionally, as demand grows, the network supports priority load management, ensuring each resident has equal access and sufficient charge for their needs.
The result? By using a private local network and cloud-based system, it was estimated that the total cost savings for the project was $24,000. Plus, as demand grows, the network supports priority load management, ensuring each resident has equal access and sufficient charge for their needs.
Read the full New Times Square case study to learn more on how the condo complex added 21 EV charging stations while avoiding $24K in unnecessary electrical upgrades.
Want to learn more about how EV charging software can benefit your property?
Get in touch with our team! We’re here to help.